Av Mikal Litland Eckblad og Nikolai Lexau Overland
•
18. januar 2026
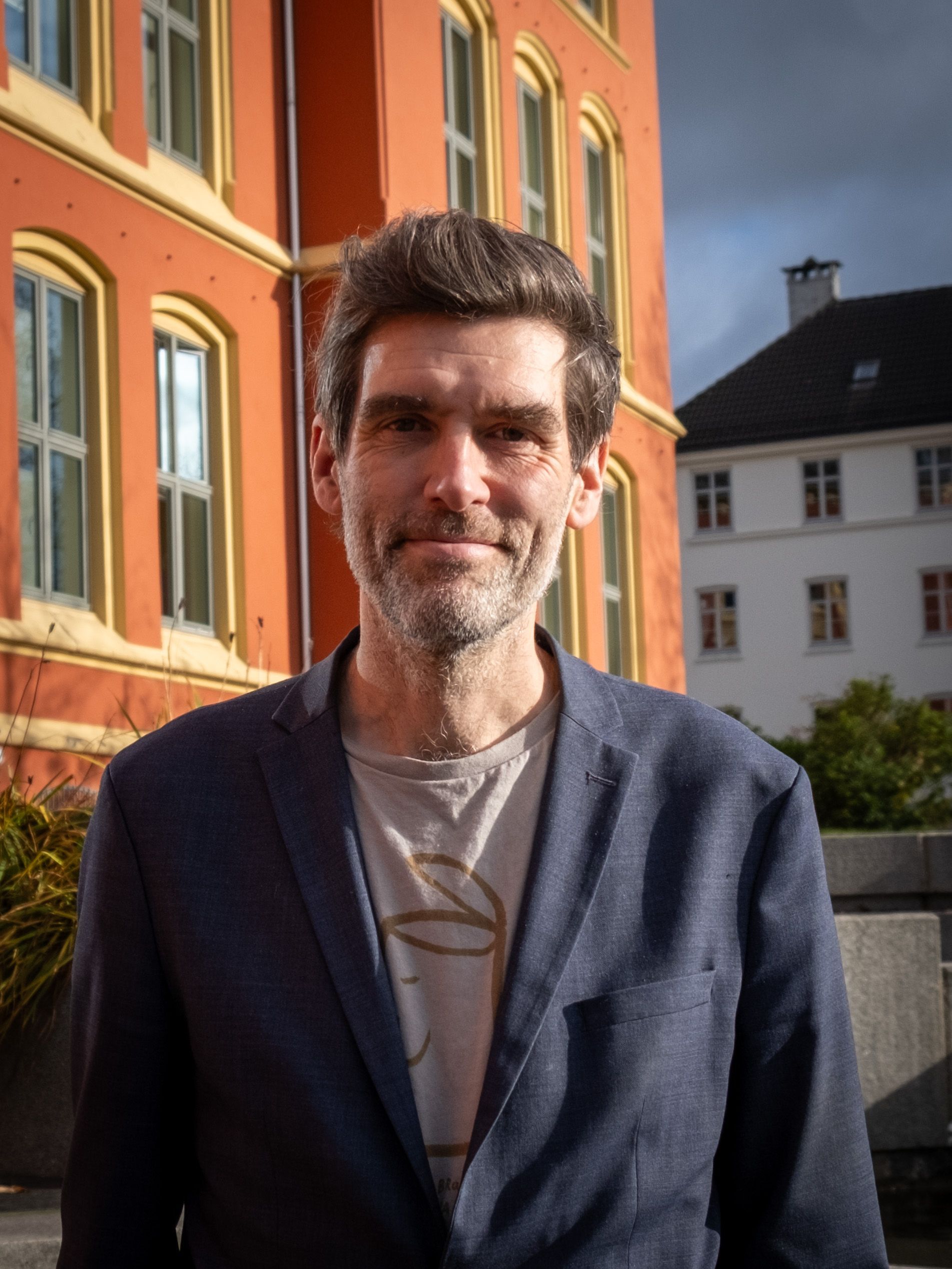
I anledning utgavetemaet «Lex, drugs and rock n´roll» har Injuria snakket med husets egne, men også en av landets fremste, professor på området, Jørn Jacobsen. Mange studenter kjenner ham som en aldri så liten juridisk rockestJørne. Andre kjenner ham først og fremst som en prinsipiell og teoretisk orientert fagperson, men er han selv enig i denne beskrivelsen? – Målet er helt klart et godt samvirke mellom teori og praksis, men det praktiske og pragmatiske tar gjerne hånd om seg selv på noe vis. Da blir det vår jobb å bidra med det som gjerne forsvinner i det daglige. Jeg tenker ikke at teori er viktigere enn praksis, men vi som er her på huset får et eget ansvar for at de større perspektivene blir ivaretatt. Desto mer interessant å grave litt i det underliggende premisset for denne Injuria-utgaven – opprør og rebelskhet! Hva tenker egentlig den prinsipielle teoretikeren om rebelske jurister – kan og bør vi gjøre «opprør» mot lovgiver og den positive retten? Hvilket ansvar har vi personlig for den retten vi håndhever? Vel, premisset er kanskje for snevert, mener han. En god jurist er tro mot jussen, men da «jussen» i en videre forstand enn vi kanskje tenker: – Vi tenker lett at jussen er det Høyesterett sier, men jussen er en samfunnsform som har flere lag enn den konkrete rettsanvendelsen. Jeg er mer opptatt av at vi har et ansvar for å ivareta jussen slik den mer grunnleggende sett er. Det krever jo at vi noen ganger er «rebelske» mot dårlige avgjørelser og ideer, og praksiser som er skadelig for rettsstaten. Det handler ikke nødvendigvis om å være rebelsk mot jussen, men derimot om å utøve god juristvirksomhet. Men tenderer vi mot å være for lojale mot lovgiver og andre institusjoner? – I et demokratisk samfunnssystem er det i stor utstrekning lovgiver som bestemmer, og det skal vi i utgangspunktet ha stor respekt for, men det er ikke ensbetydende med å la være å kritisere eller utfordre. Og, blir det for ille, krever den samme lojaliteten at man rett og slett stopper opp og gir uttrykk for at «dette går ikke». Blind systemlojalitet der vi slutter å stile spørsmål er ikke noe vi bør streve etter – det minner mer om umyndighet enn lojalitet. Han utdyper; – Jeg har stor respekt for Høyesterett som institusjon, men når man har arbeidet med juss en tid, ser man etter hvert at også juss er en menneskelig praksis. Dommere er mennesker, og dommen preges av deres forståelse. Høyesterett sine avgjørelser står, men noen ganger var det kanskje ikke så godt tenkt? Og hvordan reagerer vi best på slike dårlige beslutninger, regler og ideer? Skal man for eksempel dele ut usladdede pornoblader1 og drive cannabiscafé2 for å endre jussen, eller er det best å skrive fagbøker, artikler og høringssvar? – Vel, sivil ulydighet kan per definisjon aldri være juridisk riktig, så i det juridiske perspektivet er det sånn sett tryggere å skrive fagbøker, artikler og drive annen form for reformorientert virksomhet. Samtidig kan jussen aldri definere hva som er etisk riktig å gjøre. Som kantianer har jeg tro på den moralsk autonome borgeren som har en plikt til å lyde egen fornuft og etiske refleksjon. Underkaster man seg Stortingets politiske beslutninger blindt, blir man heteronom og oppgir både selvstendig tenkning om, og ansvar for, din egen oppfatning av hva som er det riktige å gjøre. Men hvor går den nedre grensen? – Det må jo bli opp til den enkelte å ta stilling til. Det er vel der det blir vanskelig, da? – Ja, og det er en grense vi ikke kan regelfeste på noe vis. Du må gjøre opp din egen mening om når situasjonen blir utålelig for deg som etisk individ – og den beslutningen er et selvstendig ansvar du har som tenkende, fritt menneske. Vi vil heller ha et samfunn med litt for mange tar slike beslutninger, enn et samfunn med servile, ikke-tenkende individer, mener han. Drugs I tråd med Injurias tema for denne utgaven er det spesielt aktuelt å diskutere de mange problemstillingene som har oppstått innenfor jussen på rusområdet. Det finnes dermed ingen bedre innledning til en slik samtale enn å trekke frem den beryktede mini-rusreformen som kom gjennom Høyesterett for 3 år siden. I HR-2022-731-A gjorde nettopp Høyesterett noen litt kontroversielle og uklare steg mot en ny rettstilstand på rusområdet. Jørn var heldigvis villig til å gi oss en gjennomgang av endringene som fulgte med dommen. Hva slags endringer fulgte egentlig av denne såkalte mini-rusreformen som kom gjennom Høyesterett i 2022? Jørn er skeptisk til den rusreformen som først ble foreslått. Den tok generelt sett sikte på å skifte spor i rusreguleringen fra et straffespor til et helsespor. Denne tanken forstår han isolert sett godt. Samtidig ville en slik omlegging hatt andre konsekvenser som ikke er like gode, mener han; – Jeg er litt redd for en modell der man i praksis ikke tar tak i markedet som bygger seg opp, eller allerede har bygd seg opp i tilknytning til salg av rus. Man kan godt si at det er ulovlig å være i besittelse av rus, men hvis det ikke har konsekvenser, er det i realiteten en godkjennelse av markedet, og den effekten er jeg veldig redd for. Jørn påpeker at pengene fra narkotikaindustrien uansett vil gå til kriminelle miljøer som vil bruke pengene på andre tvilsomme aktiviteter. Derfor mener han at verken et straffespor eller et helsespor for bruk i seg selv vil løse de større problemene. I juni 2025 ble det enighet om en rusreform fra Stortinget. Denne reformen dempet bruken av straff ved at forenklet forelegg ble hovedregelen for bruk og besittelse. Jørn tenker det er et steg i riktig retning, men at denne reformen likevel ikke innebærer noe mer gjennomgripende endring sammenlignet med den underliggende jussen som allerede eksisterte etter høyesterettsdommen fra 2022. Reformen fra Stortinget og Høyesterett ville ikke egentlig ta tak i det underliggende problemet bak rusmisbruk, mener Jørn. På spørsmål om hva man burde gjøre, var er klinkende klar; – Hvis dette skulle være gjort forsvarlig måtte vi egentlig ha hatt en modell à la det vi har for alkohol. Rusproblemet må løses gjennom en eller annen form for statlig legalisering, forklarer han; – Det må finnes lovlige måter å anskaffe seg på, typisk et monopol, og så må du ha sanksjoner for å gå utenfor det lovlige markedet. Hvis du først skal gjøre disse grepene så må du gjøre det mer helhetlig. Jørn påpeker at hvis staten legaliserer rus på en forsvarlig måte har staten i stor grad “satt spillereglene”. Det vil da bli lettere å regulere det å ta i bruk de illegitime markedene. Han er likevel tydelig på at en eventuell legalisering må gjøres kontrollert, og betrakter utviklingen i norsk rett som gradvise steg i så måte. – Det er i politikkens natur å behandle krevende spørsmål gradvis og stegvis. Jørn avslutter om rus med en enkel beskjed; – Jeg tror ikke man er ferdig med reguleringen på rusfeltet. Sex Den nye samtykkeloven – og da særlig «bare ja er ja»-modellen i strl. § 291 (1) – har vært og er et hett diskusjonstema. Vi ber Jørn gi oss problemstillingene med teskje. Hva er egentlig bakgrunnen for diskusjonen? Jørn forklarer at seksuallovbruddene tidligere vernet allmennheten og ærbarheten, mens selvbestemmelsesretten i større og større grad har kommet i fokus. Nyere lovreformer har endret seksualstraffebudene i denne retningen, og de fleste har handlet om å utvide voldtektsstraffebudet – det har «vokst». – Sammen med fremveksten av selvbestemmelsestankegangen, har man i økende grad sett behov for å markere krenkelser av denne selvbestemmelsesretten med bruk av voldtektsbegrepet. Utviklingen har gått mot å anse all seksuell omgang med noen som ikke har sagt ja som voldtekt. Straffelovens kapittel om seksuallovbrudd er imidlertid et system av ulike straffebud mot ulike seksuelle krenkelser, alt etter hvor alvorlige de regnes for å være. Juridisk sett er voldtekt bare en av mange seksualforbrytelser. At selvbestemmelsesretten er viktig, er alle enige om. Men, spør han; – Hvor mange tilfeller som innebærer brudd på denne selvbestemmelsen skal regnes som voldtekt? Her er det ulike syn. Noen vil ha en modell som vi nå har fått [«bare ja er ja»-modellen, red.anm]. Andre – inkludert meg – har vært skeptiske til dette. Jeg, på samme måte som Straffelovrådet, har foreslått å sette innslagspunktet for voldtekt ved seksuell omgang ved noen som har motsatt seg det [«nei er nei»-modellen, red.anm.]. Der er det ulike syn, avhengig av hvordan man ser på de prinsipielle spørsmålene og hva som er god juridisk regulering. Den loven vi nå har fått synes ikke jeg er så god. Hvilke effekter ønsket man og hvilke effekter, tilsiktede og utilsiktede, tror du samtykkeloven kommer loven til å få? – Dette blir nødvendigvis spekulativt. Loven vil etter alt å dømme ha en sterk symboleffekt. Alle er enige i at seksuelle krenkelser er et alvorlig problem, og at tiltak som reduserer slike er bra. Jørn er mer bekymret for hvilke effekter loven vil ha for strafferettens håndtering av problemstillingen. – Det er nå mer utydelig hva som skal regnes som en voldtekt, og jo mer utydelig dette er fra lovgivers side, jo større ansvar får påtalemyndigheten og domstolene for å regulere dette selv fra sak til sak. Hvorfor blir det vanskeligere å definere voldtekt nå enn tidligere? – Seksualitet er et felt der folk normalt sett interagerer på mer subtile måter – mye kan være underforstått og handle om relasjonens karakter og dynamikk. Den seksuelle interaksjonen er gjerne «diffus» og kan bestå av en kompleks og ustrukturert samhandling med større rom for utydelig kommunikasjon og feiloppfatninger. Hvor skal man da sette målepunktet for når situasjonen går fra bra til dårlig sex, og videre derfra til et straffbart overgrep som gir mange års fengsel? Mange kan ha en intuitiv oppfatning av hva som er god og dårlig sex, men grensen mot en straffbar voldtekt må ha et tydelig målepunkt som vi mangler i dag. Dette avspeiler seg i at ren passivitet etter en skjønnsmessig vurdering noen ganger kan utgjøre et samtykke, men andre ganger ikke. Han følger opp: – Jo mer utydelig definisjonen blir, jo mer faller ansvaret på påtalemyndigheten for å plukke ut de riktige sakene. Litt tabloid, men kan vi få «two stars and a wish/two wishes and a star» for samtykkeloven? – Jeg tror påtalemyndigheten og domstolen vil gi loven et forholdsvis fornuftig nedslagsfelt, men det er jo ikke egentlig deres oppgave. Det er lovgivers ansvar å avgrense de viktigste forbrytelsene klart og tydelig – det følger også av lovskravet at man i de fleste tilfeller kan avgjøre selv om handlingen er straffbar. Det synes jeg ikke denne loven lever opp til. Nå ligger ballen hos Høyesterett, og de får en viktig jobb med å trekke de nærmere grensene, mener Jørn. Foruten manglende forutberegnelighet er Jørn bekymret for en backlash-effekt der en utydelighet i loven virker kontraproduktivt ved at rettsvesenet blir utydelige i sin praktisering og store ressurser i strafferettsapparatet bindes opp i lange prosesser og ankesaker. Han viser til backlash-effekten ved innføringen av minstestraff, som mange mener fikk urimelige utslag og virket mot sin hensikt. – Et rettsapparat som er både ryddig, konsistent, forutsigbart og har rimelige og proporsjonale reaksjoner er det beste systemet for å motvirke seksuelle krenkelser. Desto mindre tvil det er om regelen, og desto tydeligere og tryggere rettssystemet er, desto sterkere vil det virke i denne sammenhengen. Han runder av: – Det er jeg mest redd for nå; at man får masse kontroverser og diskusjoner om loven som gjør kampen mot seksuelle krenkelser en bjørnetjeneste. Det er ikke alltid at det sterke symbolske uttrykket styrker en på sikt. I det personlige Jørnet I tråd med utgavetemaet følte vi oss nesten forpliktet til å stille Jørn et par tematiske og personlige spørsmål. På spørsmål om favorittrusmiddel – i vid forstand – svarer han kontant; – Det er Brannkamp, et par timer på stadion. I likhet med mange på fakultetet både i studentmassen og blant professorene (ja, vi ser på deg, Giertsen), håper også Jørn på bergensk seriegull hvert år. Er det en forbindelse mellom professoregenskaper og entusiasme for Brann fotballklubb, hvem vet? Injuria tar imot bidrag fra skribenter som ønsker å gjøre en empirisk studie av spørsmålet. Utgavetamet spiller på uttrykket “Sex, Drugs and Rock & Roll” som symboliserer ungdomsopprør. Har Jørn hatt en fase med rebelsk oppførsel i sine yngre år? Jørn måtte innrømme at han selv ikke var særlig opprørsk i sin ungdomstid, men; – Jeg er vesentlig mer opprørsk i dag enn da jeg var ung. Altså, jeg er mer forbanna nå enn jeg var da. Jeg reagerer mer mot en god del av de tingene som skjer i vår samtid, og har ganske sterke meninger om det. Da han var ung, så verden ut som den var på vei mot et bra sted. Det var kanskje ikke så stort, eller den gang synlig behov for ungdomsopprør på den tiden. Han mener likevel at dette har endret seg i nyere tid; – Nå er det skikkelig mange ting vi bør reagere mot. Det finnes både udemokratisk oppførsel og urettferdig ulikhet i verden, som man på en måte nesten aksepterer. Burde vi som jusstudenter være mer kritiske, mer opprørske? Rett og slett litt surere? – For det første syns jeg at studiet vårt skulle vært mer opprørsk. Den type jurister vi trenger i dag, er jo jurister med integritet, som står for noe. Jørn ble værende som professor på jussen etter utdanningen sin. Som professor og teoretiker er man gjerne av de mer opprørske personlighetene innenfor jussen. Mange på jusstudiet er gjerne mer interessert i å bli advokater i store firmaer eller anerkjente dommere. Syns du flere jusstudenter burde se andre veier innenfor jussen enn bare advokat og dommer? Det er jo en veldig personlig ting. Det fantastiske med jussutdannelsen er at den kan brukes på så mye forskjellig. Men hvis man har lyst til å påvirke verden der ute, så er det definitivt mange andre spor som er verdt å følge. Jørn påpeker at det ofte er de vågale og litt opprørske juristene som er med på å forme fremtidens rett og rettssystem. Denne oppgaven er ekstremt viktig, mener han. Jørns største rettspolitiske kjepphest er nemlig nettopp det at man aldri skal “underskatte verdien av systematisk, teoretisk tenking for jussen”. Det er, forklarer han, det som har formet jussen vi kjenner i dag. Helt til slutt ba vi Jørn om å gi oss sine beste studietips; – Det beste studietipset, det er et ganske kjipt tips, men ganske enkelt. Når du skal begynne å jobbe med et nytt fag, les jævlig mye. Til de av våre lesere som forventet en magisk trylleformel som skulle fikse alle studieproblemene, må vi dessverre beklage. Jørn forklarer at det viktigste i starten av et nytt fag er å absorbere informasjonen, plukk opp boka og sett på kaffetrakteren. – Folk er så imponert over kunstig intelligens. Men hva er kunstig intelligens? Jo, det er jo et forsøk på å designe noen maskiner som avspeiler vår intelligens! Se på det som hjernen din gjør hvis du mater den med store mengder data. De prosessene som skjer da er helt fantastiske! Det fins ingen annen måte å bli skikkelig bra på et fag, tror jeg, enn å bare jobbe og lese masse. Hva er ditt beste tips til eksamen da? Hvis du i første del av studiet bruker masse tid på å mate hjernen informasjon, så er det andre steget, når man nærmer seg eksamen, å slutte og mate og heller få distanse og perspektiv. Klapp igjen boka og alt sånt. Sørg for å ha gjort den tunge jobben lenge før. Gå en tur på Ulriken og se utover byen, og så få dette store perspektivet på ting. Organiser tankene dine. Da er du klar til eksamen! Vi runder av med en siste oppfordring fra en av jussens mer opprørske professorer. – Det ligger litt i jussens natur at vi skal tenke likt og alt mulig sånt. Men et sunt rettsfellesskap er noe mer. Det nærer av en mengde av litt forskjellige personligheter, med litt forskjellige bakgrunner, litt forskjellige syn på ting, litt forskjellige væremåter. Sånn får vi et mangfold i jussen òg. Når alle blir for ensrettede og opptatt av å være lik alle andre, så slutter vi å tenke kreativt, vi slutter å utfordre ting. Så om jeg skal oppfordre til noe, så er det: tør å være deg sjøl. Til alle førsteårsstudentene som for ikke så lenge siden ble fortalt at målet med jusstudiet er å sørge for at alle tenker helt likt om juss; hør på Jørn!